In recent years, a new trend has emerged in the world of finance: asset tokenization. This technology promises to revolutionise how assets are bought, sold, and traded. Asset tokenization is converting physical assets into digital tokens on a blockchain network.
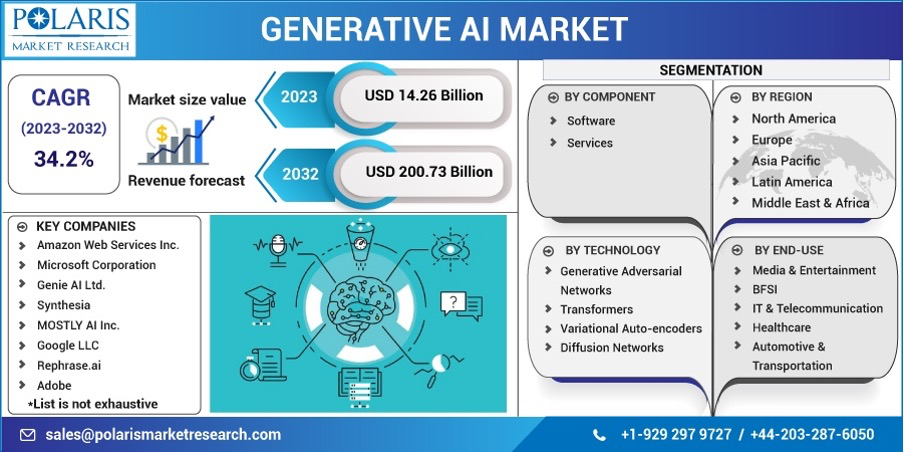
In this article, we will delve into what asset tokenization is, the technology behind it, its benefits, and its challenges. We will explore the market size of asset tokenization and how it is projected to grow in the coming years. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global asset tokenization market size is expected to reach US$5.6 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate of 19.0% from 2021 to 2026.
Asset tokenization can disrupt traditional finance by democratising investment access and increasing liquidity. However, some challenges need to be addressed, such as regulatory frameworks, security concerns, and the need for interoperability between different blockchain networks.
What Is Asset Tokenization?
The concept of asset tokenization is relatively new, emerging in the early 2010s with the development of blockchain technology. The first asset to be tokenized was Bitcoin, a digital currency that uses blockchain technology to record transactions and create new units.
However, it wasn’t until later that other assets began to be tokenized. In 2017, a company called tZERO became the first to launch a regulated security token trading platform, allowing for tokenizing assets such as real estate, private equity, and debt.
Asset tokenization is a process that involves turning physical assets, such as real estate, art, or commodities, into digital tokens that can be bought and sold on a blockchain network.
Think of it like a digital version of a stock certificate. Like owning a share of a company through a stock certificate, you can now own a fraction of an asset through a digital token. For example, instead of buying an entire house, you can own a fraction of that house through a digital token.
This is important because it allows for fractional ownership, making it easier for people to invest in assets that were previously only available to large institutional investors. It also increases liquidity, which means buying and selling these assets is easier and creates new investment opportunities for people who may not have had access to them before.
As technology evolves and becomes more accessible, asset tokenization is likely to become an increasingly important part of the financial landscape.
Asset Tokenization Technology
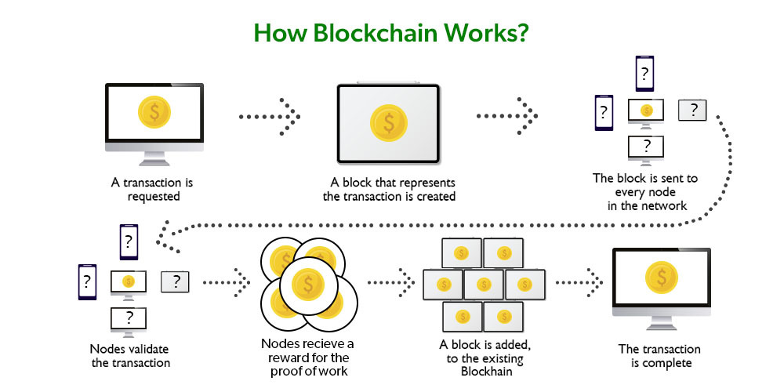
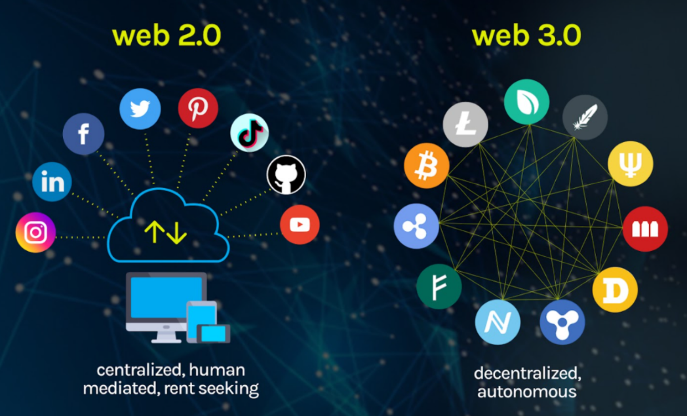
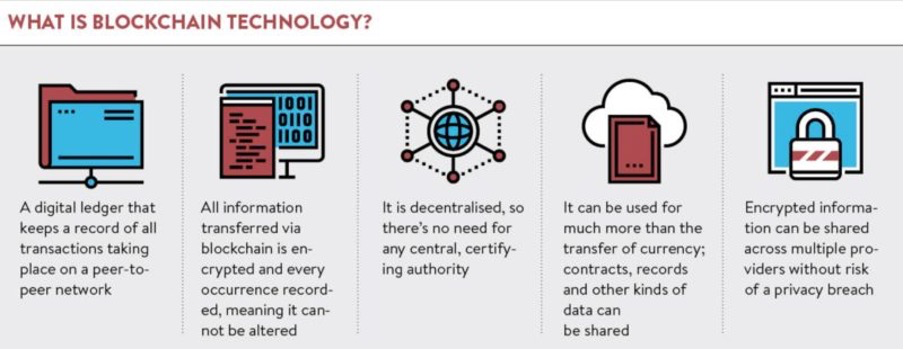
The technology behind asset tokenization is based on blockchain, a decentralised digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Blockchain technology allows for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof transactions, making it an ideal platform for asset tokenization.
Like cryptocurrencies, digital tokens can be bought and sold on the network. Below is an overview of the process.
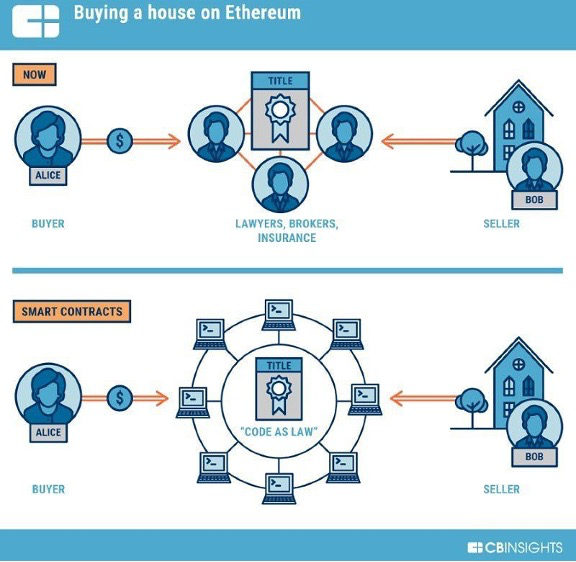
To tokenize an asset, a smart contract is created on the blockchain that defines the terms of the investment, such as the ownership structure and the rights and responsibilities of the investors. This smart contract is then used to create digital tokens representing fractional ownership in the asset.
These digital tokens are then traded on the blockchain network, just like cryptocurrencies. Investors can buy and sell these tokens on exchanges or through peer-to-peer transactions. As real-world assets back the tokens, their value is tied to the underlying asset.
For example, imagine a real estate developer who wants to raise capital for a new development project. They could tokenize the development project by creating digital tokens that represent fractional ownership. These tokens could then be sold to investors on a blockchain network, providing the developer with the capital needed to fund the project. Investors would then own a portion of the development project and receive a share of the profits when the project is completed and sold.
Another example is the tokenization of fine art. Artwork can be challenging to value and sell due to its subjective nature. By tokenizing fine art, investors can buy and sell fractional ownership in the artwork, making it a more liquid investment. Additionally, the blockchain ledger provides a transparent ownership record, reducing fraud risk.
The Benefits
Asset tokenization offers several benefits over traditional financial transactions. One significant advantage is increased liquidity. Traditional investments, such as real estate or private equity, can be difficult to buy and sell due to high transaction costs and limited market access. Asset tokenization allows for fractional ownership, which means investors can buy and sell smaller portions of an asset, making it easier to liquidate their investment.
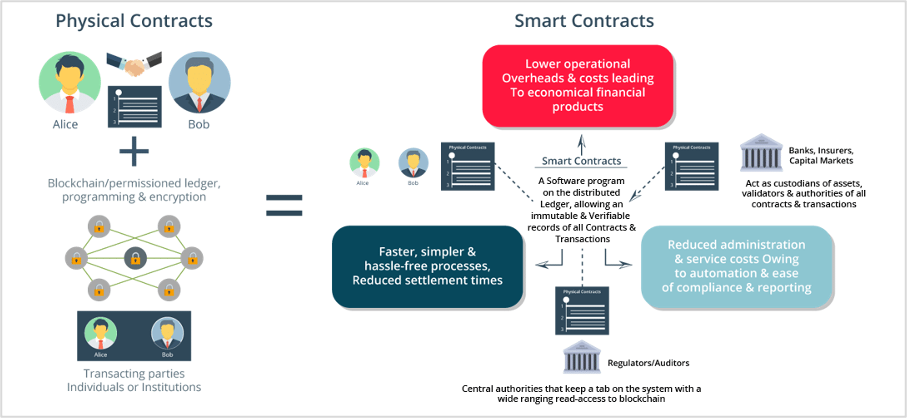
Another benefit is increased transparency. The blockchain ledger used in asset tokenization provides a transparent record of ownership, reducing the risk of fraud or errors. The ledger is immutable, meaning once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered, providing a secure and tamper-proof record of ownership.
Asset tokenization also offers greater accessibility to a broader range of investors. Previously, real estate or private equity investments were only available to large institutional investors or accredited individuals. Tokenization allows for fractional ownership, meaning investors with smaller amounts of capital can participate in investments that were previously out of reach.
In addition, asset tokenization offers greater efficiency in the investment process. Traditional investments often require a complex and lengthy transaction process involving intermediaries such as brokers and lawyers. Asset tokenization eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and time.
Asset tokenization offers numerous benefits over traditional financial transactions, including increased liquidity, transparency, accessibility, and efficiency.
The Risks and Challenges
While asset tokenization offers numerous benefits, it also presents risks and challenges.
One of the main risks is the potential for regulatory uncertainty. Asset tokenization is a relatively new concept, and regulations are still developing. Different countries have different laws regarding the use of blockchain technology, and there is no universal framework for asset tokenization. This lack of regulatory clarity can create uncertainty for investors and companies and may slow the adoption of asset tokenization.
Another challenge is the risk of hacking or security breaches. Blockchain technology is secure and tamper-proof but not invulnerable to attack. If a hacker gains access to the blockchain ledger, they could alter transaction records, steal assets, or compromise investor information. Companies must take appropriate security measures to mitigate this risk.
Asset tokenization may also face challenges related to market acceptance. Despite the potential benefits, there may be resistance to investing in digital assets. Investors may be wary of the technology or not fully understand the implications of investing in a digital token. Companies and platforms offering asset tokenization must educate investors and build trust in the technology.
Finally, asset tokenization may face challenges related to scalability. As more assets are tokenized and traded on blockchain networks, the volume of transactions could potentially overwhelm the system, leading to slower processing times and increased costs. Blockchain technology is still in its early stages, and it remains to be seen whether it can handle the scale required for widespread asset tokenization.
Companies Using Asset Tokenization
There are several companies and platforms that are using asset tokenization in various ways. Here are some examples:
Harbor. Harbor is a blockchain platform that specialises in tokenizing private securities. The company’s platform allows issuers to offer securities to a wider range of investors, with fractional ownership, lower transaction costs, and increased liquidity. Harbor has tokenized assets such as real estate, private equity, and venture capital.
Securitize. Securitize is a blockchain platform that enables the tokenization of traditional securities such as stocks, bonds, and derivatives. The platform allows issuers to offer securities to a wider range of investors, with greater efficiency and transparency. The company has worked with several companies to tokenize securities, including Blockchain Capital and SPiCE VC.
tZERO. tZERO is a regulated platform for trading security tokens. The platform enables the trading of tokenized assets such as private equity, real estate, and debt securities. tZERO offers increased transparency, lower transaction costs, and increased liquidity for investors.
Vertalo. Vertalo is a blockchain platform that enables the tokenization of alternative assets such as private equity and real estate. The platform offers a suite of tools for issuers to manage their tokenized assets, including compliance tools, investor management, and cap table management.
Closing Thoughts
Asset tokenization is a relatively new concept, but it can potentially revolutionise the financial industry in the coming decade. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and regulations around tokenization become more explicit, we can expect to see significant growth in the use of asset tokens.
The primary driver of this growth will be the increased demand for alternative investments. Asset tokenization allows investors to access alternative investments, such as art, real estate, private equity, and venture capital, with lower transaction costs and greater efficiency.
In addition, we can expect to see continued innovation in the asset tokenization space. New platforms and technologies will emerge, offering greater functionality and efficiency for tokenized assets. This innovation will help to reduce transaction costs further, increase liquidity, and improve the overall user experience for investors.
However, some challenges must be overcome for asset tokenization to reach its full potential. These challenges include regulatory uncertainty, security risks, market acceptance, and scalability. Companies and regulators must work together to address these challenges and create a framework supporting asset tokenization growth.
In conclusion, the future of asset tokenization is bright, with significant growth expected in the coming decade. As blockchain technology evolves and regulations become more evident, we expect to see widely increased adoption of asset tokens as investors search for new ways to diversify their portfolios.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is solely the author’s opinion and not investment advice – it is provided for educational purposes only. By using this, you agree that the information does not constitute any investment or financial instructions. Do conduct your own research and reach out to financial advisors before making any investment decisions.
The author of this text, Jean Chalopin, is a global business leader with a background encompassing banking, biotech, and entertainment. Mr. Chalopin is Chairman of Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The co-author of this text, Robin Trehan, has a bachelor’s degree in economics, a master’s in international business and finance, and an MBA in electronic business. Mr. Trehan is a Senior VP at Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this text are solely the views of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect those of Deltec International Group, its subsidiaries, and/or its employees.