Integrating hologram technology and AI-based chatbots is an exciting new frontier in digital communication. Hologram technology provides a new way to interact with information and data, while AI-based chatbots are changing how people communicate with businesses and organisations. Together, these technologies offer unique opportunities for organisations to engage with customers, employees and other stakeholders in more meaningful ways.
The market for hologram technology and AI-based chatbots is snowballing. According to a report from ResearchAndMarkets.com, the global holographic display market will reach US$13.5 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 26.8% from 2020 to 2026. Meanwhile, the global AI-based chatbot market is expected to reach US$1.3 billion by 2024, growing at a CAGR of 24.3% from 2019 to 2024.
What Is Hologram Technology?
Hologram technology is a cutting-edge digital visual solution that allows users to project three-dimensional images into real-world environments. The technology uses light and projection systems to create an illusion of a solid object, which can be viewed from multiple angles and appears to have depth. Holograms can be used for various applications, including entertainment, advertising, and educational purposes.
One of the significant benefits of hologram technology is that it can help businesses to stand out and capture the attention of their customers. Using holograms to showcase their products, companies can offer a unique and engaging experience that can differentiate them from their competitors. For example, hologram technology can be used to create interactive product displays that allow customers to explore a product from all angles, providing a more immersive experience.
Another benefit of hologram technology is that it can be used to improve the efficiency of communication between employees and customers. With hologram technology, employees can remotely participate in meetings and presentations, allowing them to connect with colleagues and customers from anywhere in the world. Additionally, holograms can be used to conduct virtual product demonstrations, making it easier for businesses to showcase their products and services to customers.
Furthermore, hologram technology can also be used to improve training and development opportunities for employees. With holograms, employees can receive hands-on training and experience simulations in a controlled and safe environment. This type of training can be beneficial for industries such as construction, aviation, and healthcare, where hands-on training is required to ensure the safety and well-being of employees and customers.
What Are AI-Based Chatbots?
AI-based chatbots are computer programs designed to simulate human conversations with users. They use artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to understand and respond to user requests in natural language. Chatbots break down the user’s input into individual words and phrases and then analyse them to determine the user’s intent. Based on the intent, the chatbot selects a response from a predetermined list of options or generates a response using deep learning algorithms.
One of the key benefits of using AI-based chatbots is that they can simultaneously handle a large volume of customer interactions, 24/7, without human intervention. This means that customers can receive fast and efficient support outside business hours. Chatbots also offer a convenient and accessible way for customers to interact with a company, as they can be integrated into websites, messaging apps, and other digital platforms.
Some of the companies that are using AI-based chatbots effectively include:
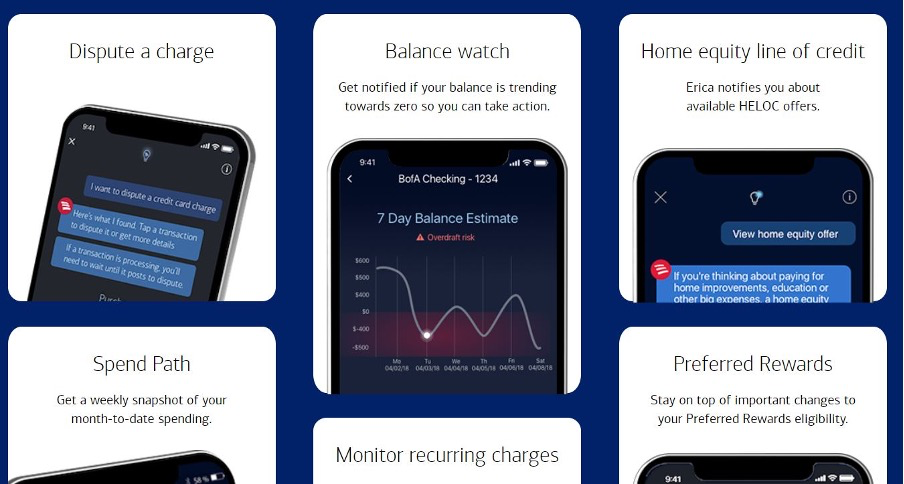
Bank of America. Bank of America’s virtual assistant, Erica, uses natural language processing and machine learning to help customers manage their finances and answer questions about their accounts.
H&M. The fashion retailer has integrated chatbots into their customer service operations, allowing customers to use messaging apps to receive fast support with their orders and returns.
Sephora. Sephora’s chatbot, named ‘Sephora Assistant’, uses AI to provide customers with personalised beauty recommendations and product information.
Overall, AI-based chatbots offer businesses a cost-effective and efficient way to interact with customers. Their capabilities constantly improve as advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning continue.
Hologram Technology and AI-based Chatbots: Working Together
Hologram technology and AI-based chatbots can work together to provide a more immersive customer experience. With hologram technology, a computer-generated 3D image of a person or object is projected into the real world, giving the illusion of a physical presence. By integrating AI-based chatbots into this technology, businesses can create virtual assistants that can interact with customers in real time and provide personalised support.
For example, a customer might approach a holographic display and ask questions such as ‘What are your hours of operation?’ The AI-based chatbot would recognise the customer’s voice, process the request, and respond appropriately through the holographic image. The chatbot can also use the customer’s previous interactions and preferences to personalise the interaction and provide a more tailored experience.
One company that is using this technology effectively is Lowe’s, the home improvement retailer. Lowe’s has developed a virtual assistant called ‘The Lowe’s Holoroom’, which uses holographic technology and AI-based chatbots to help customers plan and visualise their home improvement projects.
Google rolled out a project in 2021 that utilises holograms in chats. According to the futuristic idea, users can transform into life-size 3D holographic replicas of themselves in virtual chat booths, giving the impression that they are in the same room as you.
The Challenges
There are several challenges in combining hologram technology with AI-based chatbots, including:
Technical complexity. Hologram technology requires specialised hardware and high-performance computing resources, making it challenging to integrate with AI-based chatbots. Additionally, the development of holographic displays that can interact in real-time with AI-based chatbots is still in its early stages.
Cost. Implementing hologram technology can be expensive, which may limit its widespread adoption. This high cost can make it difficult for companies to integrate hologram technology with AI-based chatbots, as both technologies require significant investment.
Interoperability. Hologram technology and AI-based chatbots are separate technologies, each with its own standards and protocols. Integrating these technologies seamlessly and effectively can be challenging, as they may not be designed to work together.
User experience. Creating a seamless and intuitive user experience that effectively combines hologram technology and AI-based chatbots can be difficult. A key challenge is ensuring that the technology is easy to use and provides a consistent and engaging experience for customers.
Privacy and security. Integrating hologram technology and AI-based chatbots raises privacy and security concerns, as the technology can collect and store sensitive customer data. Ensuring the security and privacy of this data is a critical challenge that must be addressed.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of combining hologram technology with AI-based chatbots are significant. As technology advances, we will likely see continued innovation and progress in this field.
Closing Thoughts
It is difficult to say whether hologram technology is the future of AI-based chatbots, as these technologies are constantly evolving. While hologram technology has the potential to provide a more interactive customer experience, it also presents several challenges, such as the need for specialised hardware and high-performance computing resources. Additionally, the cost of implementing hologram technology is currently high, which may limit its widespread adoption.
That being said, AI-based chatbots and hologram technology are two of the most promising advancements today, and they have the potential to complement each other in many ways. As both technologies continue to advance, we will likely see more companies exploring the possibilities of integrating them to create new and innovative customer experiences.
While hologram technology may play a role in the future of AI-based chatbots, it is too soon to predict the exact trajectory of this field. The integration of these technologies will continue to evolve, and we will likely see various approaches to combining AI-based chatbots and hologram technology in the future.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is solely the author’s opinion and not investment advice – it is provided for educational purposes only. By using this, you agree that the information does not constitute any investment or financial instructions. Do conduct your own research and reach out to financial advisors before making any investment decisions.
The author of this text, Jean Chalopin, is a global business leader with a background encompassing banking, biotech, and entertainment. Mr. Chalopin is Chairman of Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The co-author of this text, Robin Trehan, has a bachelor’s degree in economics, a master’s in international business and finance, and an MBA in electronic business. Mr. Trehan is a Senior VP at Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this text are solely the views of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect those of Deltec International Group, its subsidiaries, and/or its employees.