Decentralised finance (DeFi) is rapidly revolutionising the financial industry by offering innovative financial products and services that are decentralised, transparent, and accessible to everyone. DeFi operates on blockchain technology and allows individuals to take control of their finances without intermediaries.
According to Cointelegraph, the DeFi market has seen tremendous growth, with the total value locked in DeFi protocols surpassing $70 billion in January 2023. As DeFi continues gaining momentum, it is expected to change how the world thinks about and interacts with finance.
What Is DeFi?
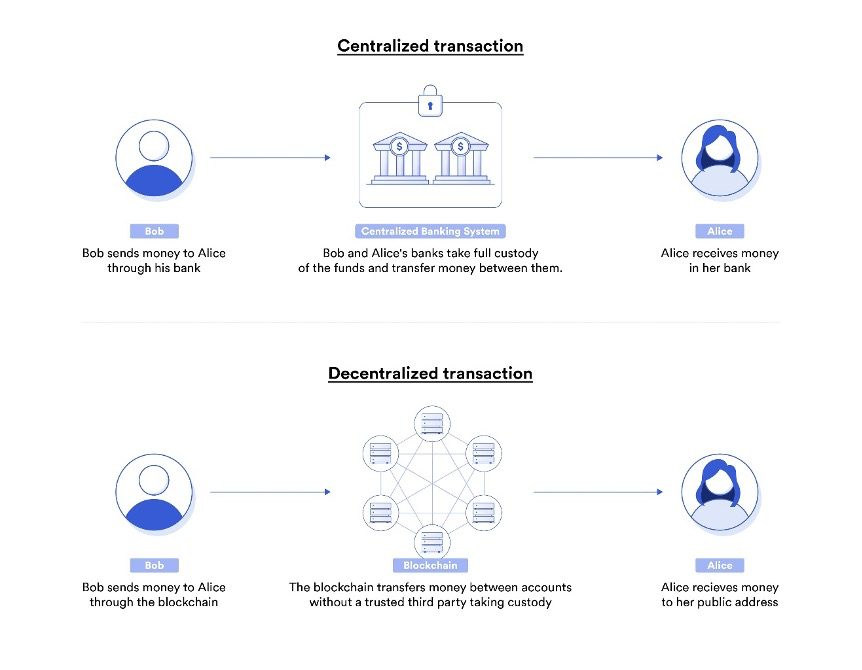
Unlike traditional finance, which relies on intermediaries such as banks and financial institutions, it is built on decentralised networks that allow for direct peer-to-peer transactions and offer more transparency, security, and accessibility.
At its core, DeFi leverages blockchain technology to create a new financial infrastructure that is open and accessible to anyone with an internet connection. This infrastructure is based on smart contracts, self-executing agreements that enforce the terms of a contract without the need for intermediaries. This means that its users can access a range of financial products and services, such as lending, borrowing, trading, and insurance, without going through a traditional financial institution.
Financial firms and institutions are taking notice and are looking to incorporate its benefits into their operations. The transparency and security offered can help to reduce the risk of fraud and increase efficiency in financial transactions.
Additionally, its decentralised nature means that it has the potential to offer financial services to individuals who are currently underserved by traditional finance, such as those in developing countries or those with limited access to conventional financial services.
How do DeFi and Blockchain Work Together?
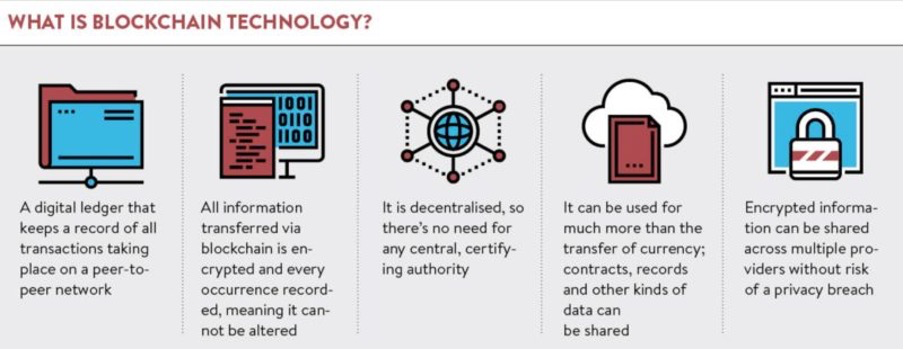
Decentralised finance and blockchain technology are two sides of the same coin, enhancing the other to create a new financial ecosystem. DeFi leverages blockchain technology to provide a decentralised and transparent infrastructure for financial transactions, while blockchain technology offers the security and immutability necessary.
Blockchain technology, the underlying technology, is a decentralised and secure ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. This decentralised nature means there is no central point of control or single point of failure, making blockchain networks highly resistant to hacking and tampering. The transparency and immutability of blockchain technology make it ideal for DeFi, as it allows for all transactions to be recorded publicly and makes it difficult for anyone to alter the records.
DeFi takes advantage of this security and transparency to offer various financial services, such as lending, borrowing, trading, and insurance, without intermediaries. For example, a sample lending platform may allow users to lend and borrow assets using smart contracts, with the platform’s underlying blockchain technology providing the security and transparency necessary for transactions. In this way, DeFi leverages blockchain technology to offer a new, decentralised financial infrastructure accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
DeFi and blockchain technology work together to create a new financial ecosystem that is decentralised, transparent, and secure. The decentralised nature of blockchain technology provides the security and transparency necessary for DeFi to function effectively. At the same time, it leverages blockchain technology to offer financial services without intermediaries. This combination has the potential to change the way the world thinks about and interacts with finance, making financial services more accessible and secure for everyone.
DeFi and Traditional Finance
Traditional finance firms need to care about DeFi because it represents a significant shift in the financial landscape. It offers a new way for people to manage their financial assets and transactions without relying on centralised intermediaries like banks. This decentralised model has proven to be secure, transparent, and accessible to people worldwide, making it an attractive alternative to traditional finance.
By ignoring DeFi, traditional finance firms risk being left behind as more people flock to decentralised alternatives. They need to stay ahead of the curve and understand the growing ecosystem to adapt and evolve their own services to meet the market’s changing demands.
Furthermore, DeFi has the potential to disrupt traditional finance and impact the bottom line of these firms. Traditional finance firms must take DeFi seriously and find ways to integrate it into their business models to remain relevant and competitive.
How Are Start-Ups Using DeFi?
Aave is a DeFi start-up that offers decentralised lending and borrowing services. The platform allows users to deposit their digital assets as collateral and then borrow other assets at a flexible interest rate without needing a central authority.
Aave uses smart contracts to automate the lending and borrowing process and ensure that each loan’s terms are transparent and fair. The platform also offers features like flash loans, which allow users to borrow funds without collateral for a short time, and liquidity pools, which enable users to earn interest on their deposited assets.
Compound is another start-up revolutionising the lending and borrowing world. The platform allows users to deposit and lend various digital assets, including cryptocurrencies, stablecoins, and non-fungible tokens.
Like Aave, Compound uses smart contracts to automate the lending and borrowing process, but it also includes a unique feature called ‘cTokens’, which allows users to earn interest on their deposited assets. cTokens are unique because they represent a user’s stake in a particular asset within the Compound platform, and their value changes in real-time based on market conditions.
Uniswap is a decentralised exchange that allows users to trade cryptocurrencies in a trustless manner. Unlike traditional centralised exchanges, Uniswap doesn’t require users to deposit their funds into a central exchange, which reduces the risk of theft and hacks. Uniswap uses a unique liquidity pool model where users can provide liquidity to the platform in exchange for a share of the trading fees.
The platform’s automated market maker algorithm ensures that users can trade token pairs without needing an order book. This makes it easy for users to trade even less popular tokens that might not be listed on centralised exchanges.
DeFi start-ups are using decentralised finance to disrupt traditional finance and offer new financial services that are secure, transparent, and accessible to people all over the world. By using smart contracts and other blockchain technologies, these start-ups are creating a new financial ecosystem free from centralised intermediaries’ limitations and restrictions.
Moving to a DeFi Model
Fidelity Investments is a traditional finance firm exploring DeFi to offer new financial services to its customers. The company has launched a new division called Fidelity Digital Assets that provide custody and trading services for cryptocurrencies, making it one of the first large traditional finance firms to embrace DeFi.
Fidelity is using DeFi to offer its customers access to new investment opportunities in the cryptocurrency market and reduce the barriers to entry that have traditionally made it difficult for institutional investors to participate in the market.
Goldman Sachs is another traditional finance firm that is exploring DeFi. The company has been actively engaged in DeFi’s value proposition and creating DeFi products. Goldman Sachs is collaborating with other businesses to develop a digital assets framework, per a press release from November 2022.
JP Morgan is another traditional finance firm that is moving into DeFi. The company has been exploring blockchain technology for several years and working on its DeFi initiatives. For example, JP Morgan initiated its first DeFi trade on blockchain in 2022. Project Guardian, a trial programme run by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) to investigate potential DeFi applications in wholesale finance markets, enabled the trade.
Traditional finance firms are exploring DeFi to offer new financial services to their customers and stay ahead of the curve in an ever-changing economic landscape. By embracing DeFi, these firms can reduce barriers to entry and offer secure, transparent, and accessible financial services to their customers.
Risks and Challenges
One of the main risks associated with DeFi is security. Since it is built on decentralised networks, it is more vulnerable to hacking and other forms of cybercrime. Smart contracts, which are used to automate the process of lending, borrowing, and trading in DeFi, are particularly vulnerable to security threats. For example, if a hacker can exploit a vulnerability in a smart contract, they can steal funds from users or manipulate the platform in other ways.
Another challenge is scalability. As more people use DeFi platforms, the networks can become congested, leading to slow transactions and high gas fees. This can make it difficult for users to participate in DeFi platforms, especially during times of high demand.
Since DeFi is a relatively new technology, there is still a lot of uncertainty about how it will be regulated in the future. Some countries have already taken steps to regulate DeFi, while others have been more cautious. This uncertainty can make it difficult for DeFi platforms to operate and discourage investors from participating in the market.
Lack of liquidity is still associated with DeFi. Although DeFi platforms have snowballed in recent years, they still have relatively small liquidity pools compared to centralised exchanges. This can make it difficult for users to trade their assets and lead to price volatility.
Finally, DeFi can also be challenging for non-technical users. Since it is built on complex technology, it can be difficult for users unfamiliar with blockchain and cryptocurrency to participate in DeFi platforms. This can make it difficult for DeFi to achieve widespread adoption and discourage users from participating in the market.
Despite these risks, by integrating the right technology, such as blockchain, DeFi will still disrupt and revolutionise the industry.
Closing Thoughts
The future of DeFi is exciting and filled with endless possibilities. In the next ten years, we can expect to see it become more accessible and user-friendly, allowing more people to participate in the market. This will likely increase the number of DeFi platforms and the size of the DeFi market.
Additionally, as DeFi grows and matures, we expect to see more innovation in the space, including new financial products and services built on decentralised networks. This will likely include everything from new forms of lending and borrowing to new insurance products and investment opportunities. Overall, the future of DeFi is bright, and we expect continued growth and innovation over the next decade.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is solely the author’s opinion and not investment advice – it is provided for educational purposes only. By using this, you agree that the information does not constitute any investment or financial instructions. Do conduct your own research and reach out to financial advisors before making any investment decisions.
The author of this text, Jean Chalopin, is a global business leader with a background encompassing banking, biotech, and entertainment. Mr. Chalopin is Chairman of Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The co-author of this text, Robin Trehan, has a bachelor’s degree in economics, a master’s in international business and finance, and an MBA in electronic business. Mr. Trehan is a Senior VP at Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this text are solely the views of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect those of Deltec International Group, its subsidiaries, and/or its employees.