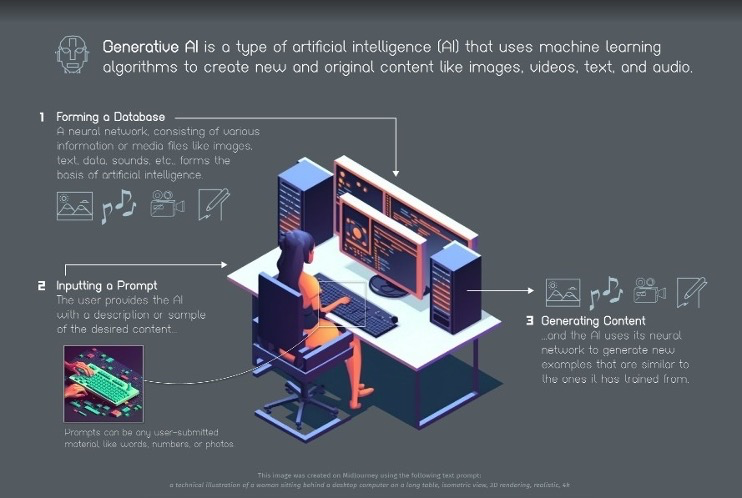
Generative AI is a rapidly developing field of artificial intelligence that has been making waves in recent years. Using advanced algorithms, generative AI can create original and often impressive content, such as images, music, and even text, without direct human input.
This article will delve deeper into generative AI, exploring what it is, how it works, and its potential uses.
Understanding Generative AI
Unlike other types of AI designed to complete specific tasks, such as image recognition or language translation, generative AI is programmed to learn from existing data and generate new content based on that information.
The key to this process is the use of deep neural networks, designed to simulate how the human brain works, allowing the AI system to learn from patterns and generate new content.
One of the most impressive aspects of generative AI is its ability to create content that is often difficult to distinguish from something a human would produce. For example, generative AI can be used to create realistic images of people who don’t exist or to generate music that sounds like it was composed by a human musician. The image below is AI-generated and not of a real person.
This has exciting implications for various industries, from art and entertainment to marketing and advertising.
Against Other Forms of AI
Generative AI is distinct from other forms because it is designed to create something new rather than simply perform a specific task. This contrasts with different types of AI, such as supervised learning or reinforcement learning, which are focused on solving a particular problem.
For example, supervised learning algorithms are commonly used in image recognition software to identify and classify objects within a given image. In contrast, generative AI can be used to create original ideas, such as realistic portraits of people who don’t exist or entirely new landscapes that have never been seen before.
Another example of a different type of AI is natural language processing (NLP), which is used to analyse and understand human language. While NLP can generate text, it is typically focused on tasks such as language translation or sentiment analysis. In contrast, generative AI can be used to create entirely new pieces of text, such as short stories, poetry, or even news articles.
Most of the AI we see today is still based on machine learning, which involves training a model on a large dataset to identify patterns and make predictions. This is done by feeding the machine learning algorithm a set of labelled data, allowing the system to learn from the data and identify patterns that can be used to make predictions on new, unseen data.
While machine learning has already had a significant impact on many industries, from healthcare to finance to transportation, the ability to create entirely new content has the potential to revolutionise these fields completely.
Ultimately, the critical difference between generative AI and other types of AI is the focus on creativity and originality.
The Benefits of Generative AI
Generative AI is a rapidly developing field with numerous potential benefits.
One industry that could improve significantly from generative AI is fashion. With the ability to generate unique designs and patterns, it has the potential to transform the fashion industry. Designers can use it to create new designs, allowing them to produce unique and eye-catching pieces that stand out from the competition. By using it, designers can also save time and resources, allowing them to focus on other aspects of the creative process.
A second industry that stands to gain is gaming. With the ability to generate unique characters, landscapes, and environments, it has the potential to revolutionise the gaming industry. Game designers can use it to create original game elements that are unique and engaging for players. It enables game designers to save time and resources, allowing them to focus on other aspects of the game development process.
Finally, generative AI has the potential to shift the healthcare industry. Using it, researchers can create new drugs and treatments, allowing them to treat diseases and illnesses. It can also be used to analyse medical images and data, allowing doctors and researchers to diagnose and treat patients more accurately. With its ability to create new content and analyse large amounts of data, generative AI can potentially transform how we approach healthcare.
Successful Case Studies
Several companies are already using generative AI to great effect in their applications. Here are a few examples:
Adobe is using generative AI to develop new tools and features for its Creative Cloud suite of products. For example, Adobe’s Sensei platform uses generative AI to analyse images and suggest improvements. The company has also used it to develop new fonts and predict which colours will be popular in the coming year.
OpenAI is a research organisation focused on advancing AI safely and responsibly. The company has developed several generative AI models, including GPT-3, a language model that can generate text that is often difficult to distinguish from something a human would write. GPT-3 has many potential applications, from natural language processing to chatbots. The revolutionary Chat GPT platform is based on these models.
IBM uses generative AI to develop new solutions for various industries, including healthcare and finance. For example, the company has developed a system to analyse medical images and provide more accurate diagnoses. It has also used it to create new financial risk models.
Nvidia is a leading provider of graphics processing units (GPUs) that are used in various applications, including gaming, scientific research, and machine learning. The company is also investing heavily in generative AI and has developed several models that can generate realistic images and even entire virtual environments.
These companies are just a few examples of how generative AI is already being used to create new opportunities and drive innovation in several industries. As the technology develops, it will be interesting to see how it is integrated into even more applications and use cases.
The Risks
While generative AI has enormous potential, several risks are also associated with the technology. One of the most significant risks is its potential to be used for malicious purposes.
For example, it can be used to create realistic-looking fake images, videos, and audio, which can be used for deception or propaganda. In the wrong hands, these tools could be used to manipulate public opinion, create fake news, or even commit fraud.
Another risk of generative AI is its potential to perpetuate biases and inequalities. Its models are only as good as the data they are trained on, and if the data is biassed, then the model will be biassed as well.
For example, a generative AI model trained on predominantly white and male data may be more likely to generate images and text biassed against women and people of colour. This can perpetuate existing inequalities and reinforce harmful stereotypes.
In one study published in 2018, researchers found that several leading facial recognition algorithms were significantly less accurate at identifying the faces of people with darker skin tones, particularly women. This bias was pervasive across multiple algorithms from different companies. The researchers attributed it to the fact that the training datasets used to develop the algorithms were overwhelmingly white and male.
A third risk of generative AI is its potential for cyberattack use. For example, generative AI can generate realistic-looking phishing emails, which can trick people into giving up sensitive information or clicking on links that download malware onto their devices. Additionally, generative AI can generate realistic-looking social media profiles, which can be used for impersonation or other online attacks.
Overall, while it has enormous potential for positive applications, it is vital to be aware of the risks associated with the technology. As the technology continues to develop, it will be necessary for developers and users of generative AI to take steps to mitigate these risks and ensure that the technology is being used responsibly and ethically. This will require ongoing research, development, collaboration, and coordination among stakeholders in various industries.
Closing Thoughts
Generative AI has made tremendous progress in recent years, and there is no doubt that the technology will continue to evolve and improve in the coming decade. One of the most promising areas of development for generative AI is in the realm of creative applications. For example, generative AI is already being used to generate music, art, and even entire literature. As technology advances, we can expect to see more creative works generated by AI and even collaborations between human and machine artists.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is solely the author’s opinion and not investment advice – it is provided for educational purposes only. By using this, you agree that the information does not constitute any investment or financial instructions. Do conduct your own research and reach out to financial advisors before making any investment decisions.
The author of this text, Jean Chalopin, is a global business leader with a background encompassing banking, biotech, and entertainment. Mr. Chalopin is Chairman of Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The co-author of this text, Robin Trehan, has a bachelor’s degree in economics, a master’s in international business and finance, and an MBA in electronic business. Mr. Trehan is a Senior VP at Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this text are solely the views of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect those of Deltec International Group, its subsidiaries, and/or its employees.