Two fundamental questions surround Web 4.0: Will virtual reality (VR) gain traction in society? What will social media look like in the future? Even if we are aware of the exponential rise of technology, it’s still challenging to forecast where we will be in ten years.
Although details are hard to predict, reviewing the past reveals a clear direction for what Web 4.0 may entail. Web 3.0 is still in its infancy, but experts are already romanticizing how Web 4.0 could change the world.
To illustrate how we arrived at the current state of Web 3.0, we will review each previous version of the internet. This article will then hypothesize on a possible Web 4.0.
Web 1.0: Beginning
The term “Web 1.0” refers to the beginnings of the internet.
Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) research initiatives helped develop protocols like TCP/IP, which enabled networked computers to communicate with one another. The study quickly earned the name “Internet.” Web pages connected to one another comprised the majority of this internet.
Web 1.0’s state was very much read-only, in contrast to the web as it is now. Since static pages made up most online pages, there were hardly any interactive features.
There will mostly be a minimalist approach to design then. Each webpage typically consisted of a combination of text and images over a background of pure white.
The internet’s initial iteration was ground-breaking. It was a brand-new system that allowed anyone with access to the system, wherever in the world, to share information.
Users have little else to do but browse the amount of information. The web eventually needed to change as more people began using the internet.
Web 2.0: Interactive
The need for online collaboration, sharing, and communication skyrocketed in the late 1990s.
Because of this, many engineers predicted a new era for the internet. “Web 2.0” is a word that was created to define this new era by writer and web designer Darcy Dinucci.
It signalled a paradigm change from static web pages to interactive web applications. People created online communities on Web 2.0 websites.
Soon, several social networking sites, blogs, wikis, and platforms for sharing material were developed. Users can now add to a website’s content instead of just reading it for the first time. It sparked the development of online shopping, where customers may not only buy and sell goods but also post reviews.
Platforms for sharing and publishing information were increasingly popular in the 2010s.
Sites like Youtube, Instagram, and Facebook have figured out how to make money off the internet’s new function as an outlet for ideas and creative expression.
Your online identity has developed into a brand-new aspect of you. With the advent of smartphones, the internet quickly became portable, making it accessible to billions of people.
This swiftly made room for the web’s subsequent expansion.
Web 3.0: Big Data and AI
Today marks the era of the big data.
These enormous platforms own vast amounts of priceless data thanks to the increasing volume of information being posted to the internet, which is now the foundation of our economy.
Data is the new oil, according to a 2014 article in WIRED Magazine. The internet’s widespread use and the amount of data have set the stage for the web’s next chapter.
The precise concept of Web 3.0 differs depending on what you read.
The World Wide Web was created by Tim Berners-Lee, who calls it a “semantic web” that provides access to an “unbelievable data source.”
According to his forecast, the web will soon be able to comprehend the intricate relationships between concepts in the real world. With a new emphasis on users interacting with artificial intelligence, Web 3.0 moves beyond human-to-human connection.
We now use this part of the internet in our everyday lives.
Thanks to algorithms, our news feeds, and suggestions are already filled with information pertinent to us. These algorithms will only get stronger as more data is gathered.
What Is Web 4.0?
The user journey is center stage and the primary focus with Web 4.0.
Most people couldn’t imagine a world without voice commands, touchscreen interfaces, or auto-correction. Despite these developments, we haven’t yet achieved a completely smooth experience.
Being constrained by how quickly we can speak or type, our thoughts require enormous effort to communicate digitally. The line between the mind and the computer should become less distinct with the next significant advancement in web usage, Web 4.0.
The “symbiotic web,” or the symbiotic contact between man and machine, is a bold prediction of Web 4.0. Soon, AI will have developed to the point where it can comprehend our own ideas and successfully browse the web.
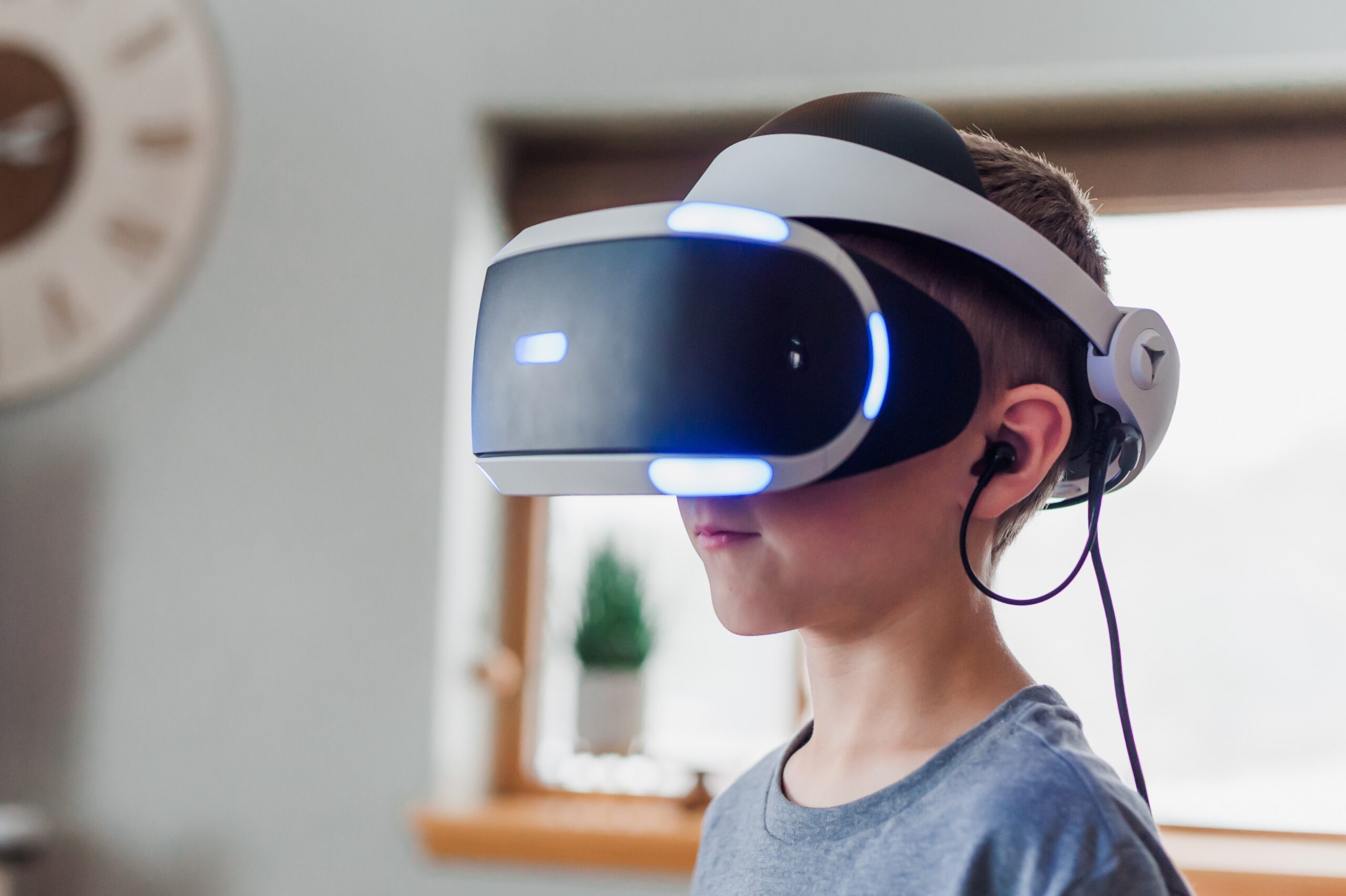
On a 2D screen, the web might not be adequately represented. Virtual reality or augmented reality technologies may supplement or form the foundation of Web 4.0. The intention remains to completely capture and provide the complete, human experience.
The internet has gradually adapted to focus on graphics and video instead of text. It’s hardly a stretch to argue that we may soon experience lifelike experiences that fully immerse users while they explore a new digital environment.
What’s the Technology Behind Web 4.0?
Several ground-breaking technologies may form the basis of Web 4.0.
Elon Musk’s business Neuralink has successfully tested wireless brain implants on animals. These brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) will soon enable us to communicate easily with and operate the gadgets around us.
Alternatively, tech behemoths are moving aggressively into the augmented and virtual reality fields. Metaverse technology is in development by businesses like Facebook and Microsoft. It could eventually replace traditional human-to-human connections.
The way we interact with the web is being revolutionized by augmented reality (AR) applications like nReal and eye-tracking technologies.
To handle the enormous quantity of input required from both the human brain and the physical world around us, Web 4.0 will need AI and sophisticated machine learning (ML) algorithms.
For instance, ML and computer vision are used by self-driving cars to understand the actual roads and potential barriers in a typical commute. This has already made significant strides.
The term “Internet of Things” describes a network of items that are equipped with sensors and software that can easily communicate with devices all around them. The popularity of smart homes has already been rising. Users can converse with their devices by speaking to virtual assistants powered by AI, such as Alexa on the Amazon Echo, and Google Assistant.
With Web 4.0, smart cities and fully AI-powered infrastructure systems may become more common.
Use Cases for Web 4.0
When we can use the power of machines to augment our thoughts, we have the potential to transform entire industries. Here are some prospective Web 4.0 applications that might be available to you sooner than you think.
Medicine
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are now being explored with the hope of assisting those with neurological disorders and similar limitations. Soon, BCIs might help speech synthesis or assist amputees in controlling prosthetic limbs.
Education and Work
The public might adopt Web 4.0 if technology improves. One day, BCIs might be employed to boost learning effectiveness or work performance. Consider a program that understands how to explain a subject specific to you and how to test you.
Because of the pandemic, remote work has become more widespread, and the breakthroughs we could make with virtual reality could alter how we operate.
Security
Pass thoughts is an alternative method of logging in to your preferred programs that is being tested by several researchers. Soon, we might be able to access our devices simply by thinking about doing so, which would be even more secure than the biometrics we currently use.
Social Media
A potential new alternate location for social gatherings is the Web 4.0 metaverse.
Connecting digitally with co-workers, friends, and family will be necessary as remote learning and remote work gain popularity. People from all over the world will be able to connect and communicate as though they were all present in the same physical area, thanks to VR and AR.
The Challenges Facing Web 4.0
As with any new technology, there are several challenges and risks associated with Web 4.0.
The use of malicious programs will still be possible with brain-computer connections. These interfaces could be targets for hacking since they hold very private information about the user.
The technology used in virtual reality is also not entirely secure. Some accounts say using VR for an extended period harms the user’s vision or may even cause seizures. A fully immersive digital experience won’t be welcomed into the masses until such safety concerns are addressed.
Data ownership becomes hazy when technologies practically become a part of us. BCIs could turn into means for tech corporations to make money off your data.
There was public uproar when Google acquired Fitbit in 2019 for $2.1 billion, giving them access to millions of consumers’ fitness data. We should be cautious about whether users are being exploited as the web becomes more user-friendly for us.
Closing Thoughts
The internet evolves as technology advances, taking into account the capabilities of modern innovation and the needs of its users.
People born after 1990 have never known a time before the internet. Children born today will never experience life without social media. The world without an enhanced mind may never be experienced by anybody born in the next ten to twenty years.
We have become more connected as the web has developed, but it has always come with a price. Future technologists and developers should be mindful of the security and privacy of their users. Whatever the outcome of these breakthroughs, one thing is sure: the future is not so far away.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is solely the author’s opinion and not investment advice – it is provided for educational purposes only. By using this, you agree that the information does not constitute any investment or financial instructions. Do conduct your own research and reach out to financial advisors before making any investment decisions.
The author of this text, Jean Chalopin, is a global business leader with a background encompassing banking, biotech, and entertainment. Mr. Chalopin is Chairman of Deltec International Group, www.deltecbank.com.
The co-author of this text, Robin Trehan, has a bachelor’s degree in economics, a master’s in international business and finance, and an MBA in electronic business. Mr. Trehan is a Senior VP at Deltec International Group, www.deltecbank.com.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this text are solely the views of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect those of Deltec International Group, its subsidiaries, and/or its employees.