As the development of Web3 continues to gain momentum, artificial intelligence is set to revolutionise how we interact with decentralised networks. Among the many AI techniques available, generative AI is gaining increasing attention for its ability to create new and unique content, which has the potential to transform the Web3 landscape.
Generative AI can be used to produce everything from text and images to music and video, providing users with a wealth of new opportunities to engage with Web3 in exciting and innovative ways.
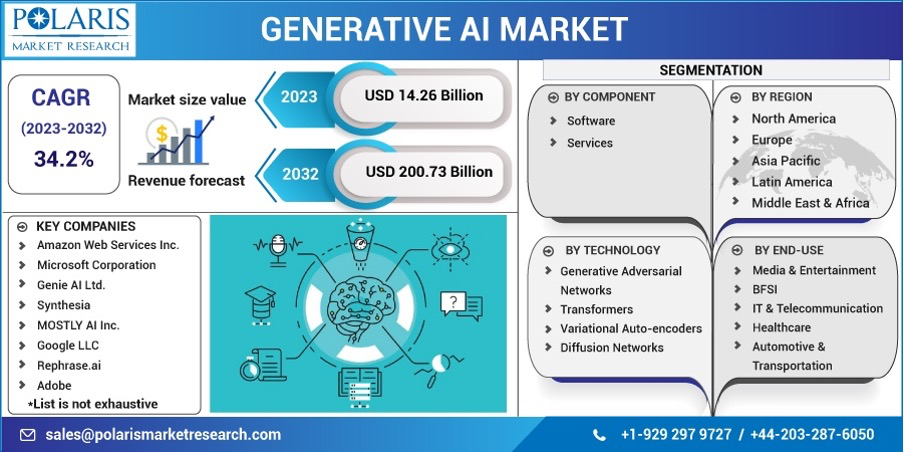
According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the generative AI market is projected to reach $200.73 billion by 2032, indicating a growing demand for this technology across various industries.
However, as with any new technology, significant challenges must be addressed, such as ensuring ethical use and mitigating potential biases. In this article, we will explore the key concepts of this form of AI and discuss its potential benefits and challenges to the Web3 ecosystem.
What Is Generative AI?
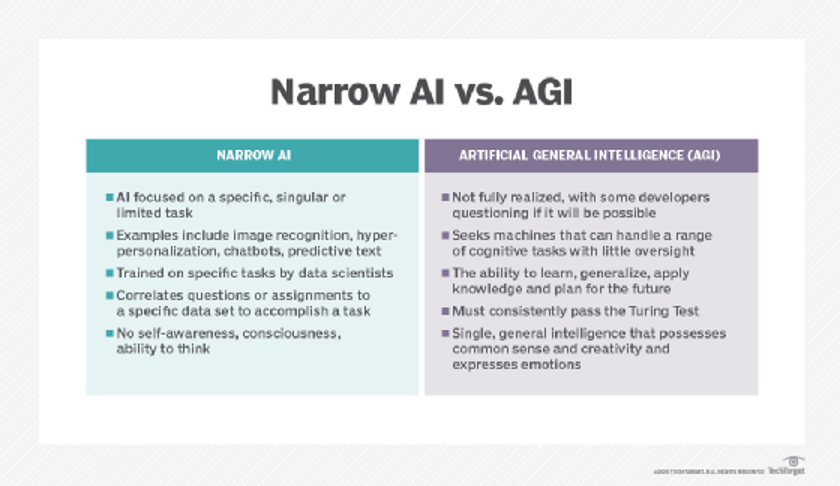
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence designed to create new and original content, such as images, text, music, and even video, without human intervention. Unlike traditional AI models, which are trained to recognize patterns and make decisions based on those patterns, generative AI is focused on generating new data that does not exist in its training data set.
This is achieved by using machine learning algorithms, such as neural networks, to analyse large data sets and identify patterns that can be used to generate new content.
Generative AI can be used in a wide range of applications, from creative industries such as music and art to more practical fields like medicine and finance, where it can be used to generate new drug compounds or financial models.
- Art: It can create original pieces of art that range from abstract to more realistic forms. For instance, The Portrait of Edmond de Belamy was created by a French art collective using generative AI, and sold at Christie’s auction house for $432,500.
- Music: AI-generated music is becoming increasingly popular, with some AI tools allowing users to create their own unique tracks. A good example is Amper Music, an AI-powered music composition platform enabling users to create and customise their original music.
- Writing: Generative AI can also be used to create original written content, including news articles and even novels. For instance, OpenAI’s GPT-3 model (Chat GPT) has been used to write articles that are difficult to distinguish from those written by humans.
- Virtual Clothing: It can also be used to create unique virtual clothing for use in the metaverse or other digital platforms. For instance, The Fabricant, a digital fashion house, has created a range of virtual clothing using generative AI.
- Video games: AI can also be used to create original video games, from procedural content generation to NPCs with their own personalities and decision-making abilities. An example is Hello Games’ ‘No Man’s Sky’, which uses procedural generation to create an entire universe of unique planets and creatures.
- Finance: AI can be used to analyse vast amounts of financial data and generate predictions and insights to inform investment decisions. For instance, the hedge fund Numerai uses generative AI models to analyse financial data and generate trading signals.
In other words, generative AI is the perfect technology to support Web3.
What Is Web3?
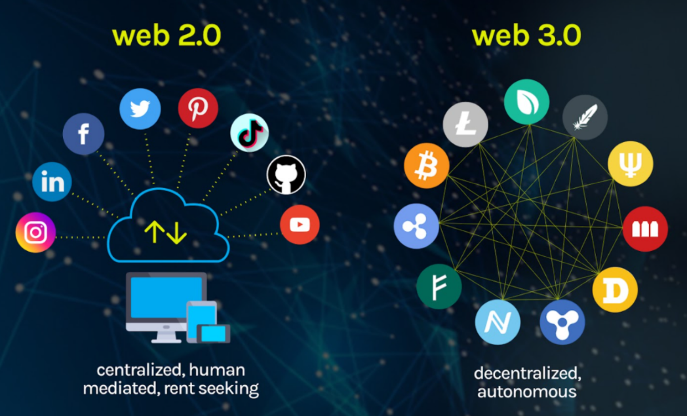
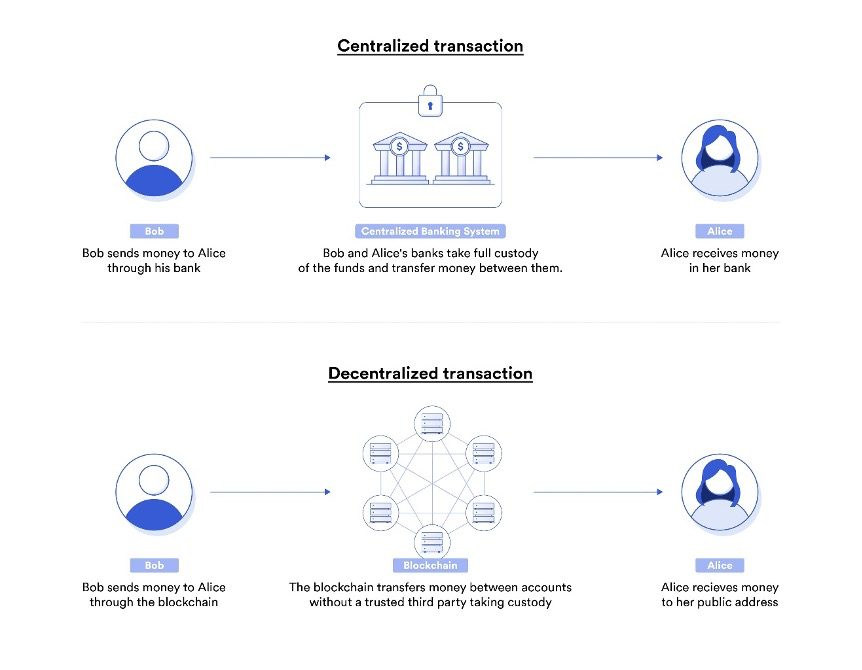
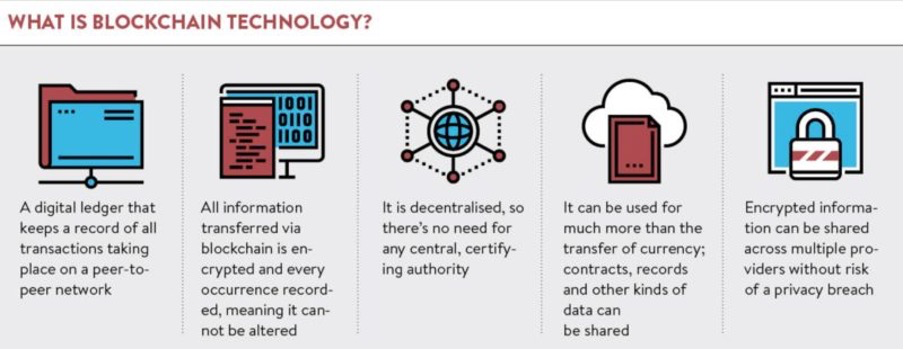
Web3 refers to the next generation of the internet, which is focused on decentralisation, security, and user control. Unlike the current Web2, which is dominated by a few large corporations that collect and control user data, Web3 is based on decentralised networks that enable users to own and control their data.
One of the key features of Web3 is the concept of the metaverse, a virtual world where users can interact with each other in real-time using avatars and digital assets. The metaverse is expected to be a key component of Web3, providing users with a new way to interact with each other and with digital content.
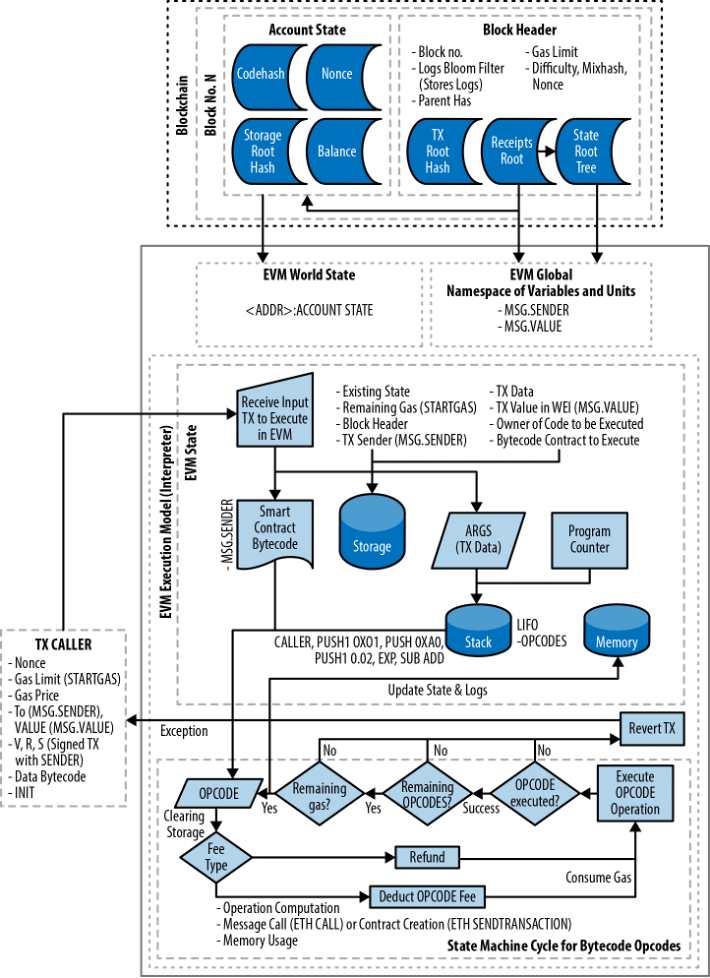
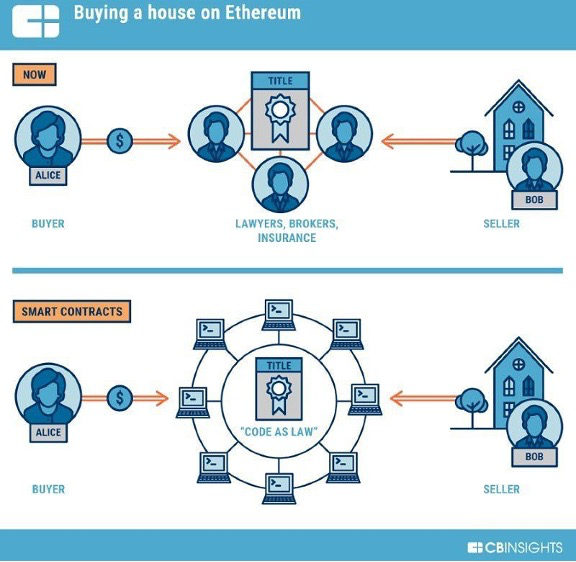
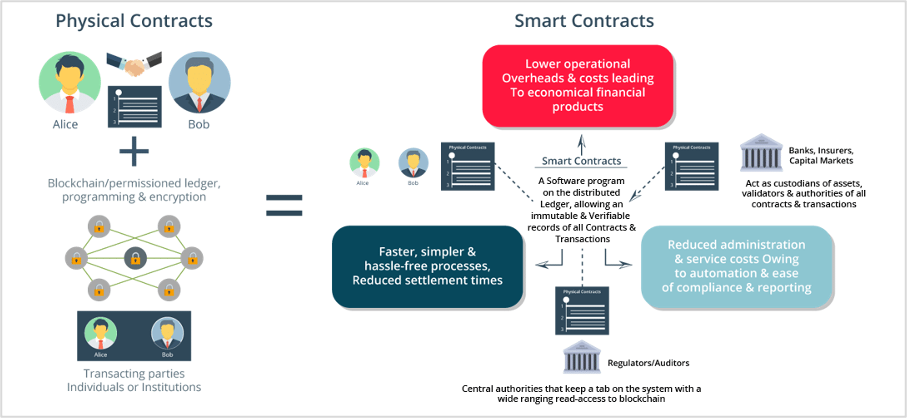
Another important feature of Web3 is smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. Smart contracts can be used to automate a wide range of processes, from financial transactions to supply chain management, without the need for intermediaries.
Generative AI can play a significant role in the Web3 ecosystem by creating new and unique digital assets for use in the metaverse and other decentralised applications. For example, generative AI can be used to create virtual clothing, art, and other assets that can be bought and sold within the metaverse.
Additionally, generative AI can be used to create smart contracts that are more efficient and secure than traditional contracts, thereby reducing the need for intermediaries. However, as with any new technology, there are also potential risks and challenges associated with using generative AI in the Web3 ecosystem, including the potential for bias and the need to ensure ethical use.
Challenges of Using Generative AI Within Web3
While generative AI has the potential to bring many benefits to the Web3 ecosystem, there are also significant challenges and risks associated with its use, particularly in the metaverse.
One of the biggest challenges is the potential for bias in the data used to train the generative AI models. If the data used to train the models is biassed, the generated content may also be biassed, perpetuating existing inequalities and marginalising certain groups. It is, therefore, essential to ensure that the data used to train the models is diverse and representative of all groups.
Another challenge is the potential for misuse of generative AI in the metaverse. For example, generative AI could be used to create realistic deepfake videos or other forms of disinformation, which could have severe consequences for individuals and society.
Furthermore, there is also the issue of ethical considerations surrounding the use of generative AI in the Web3 ecosystem. For instance, generative AI could be used to create realistic avatars of real people without their consent, raising serious privacy concerns.
There is also the question of who owns the rights to the generated content and how it can be used, particularly if it is sold for profit.
To mitigate these challenges and risks, it is essential to establish best practices and guidelines for the ethical use of generative AI in the metaverse and other Web3 applications. This includes ensuring that the data used to train the models is diverse and representative, establishing clear guidelines for using generated content and implementing effective mechanisms for detecting and preventing the misuse of generative AI.
Closing Thoughts
Generative AI has the potential to play a significant role in the Web3 ecosystem, particularly in the development of the metaverse and other decentralised applications. Generative AI can be used to create new and unique digital assets, such as virtual clothing and art, which can be bought and sold within the metaverse.
Additionally, it can be used to create smart contracts that are more efficient and secure than traditional contracts, reducing the need for intermediaries. However, there are also significant challenges and risks associated with using generative AI in the Web3 ecosystem, including the potential for bias and misuse.
To mitigate these risks, it is important to establish best practices and guidelines for the ethical use of generative AI. Despite these challenges, the future of generative AI in the Web3 ecosystem looks promising, with the potential to create innovative content while ensuring that it is used responsibly.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is solely the author’s opinion and not investment advice – it is provided for educational purposes only. By using this, you agree that the information does not constitute any investment or financial instructions. Do conduct your own research and reach out to financial advisors before making any investment decisions.
The author of this text, Jean Chalopin, is a global business leader with a background encompassing banking, biotech, and entertainment. Mr. Chalopin is Chairman of Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The co-author of this text, Robin Trehan, has a bachelor’s degree in economics, a master’s in international business and finance, and an MBA in electronic business. Mr. Trehan is a Senior VP at Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this text are solely the views of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect those of Deltec International Group, its subsidiaries, and/or its employees.