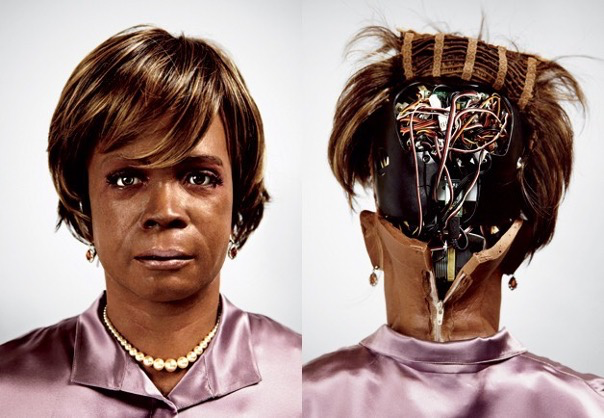
AI-powered robots’ potential to become sentient has sparked heated discussion and conjecture among scientists and technology professionals. Concerns regarding the ethical consequences of producing robots with human-like awareness are growing as AI technology improves.
The current AI in the robotics industry is worth more than $40 billion and is likely to grow in the future years. According to MarketsandMarkets, AI in the robotics market will be worth $105.8 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 19.3% from 2021 to 2026.
This article will discuss what sentience means in robotics, along with the possible benefits and challenges.
Robots and AI
Artificial intelligence refers to the ability of machines or computer programs to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. This includes perception, reasoning, learning, decision-making, and natural language processing. AI systems can be trained using large amounts of data and algorithms to make predictions or perform specific actions, often improving over time as they are exposed to more data.
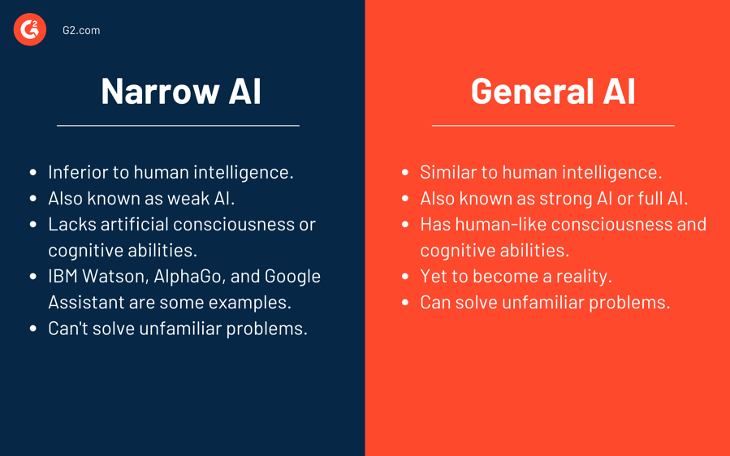
There are several types of AI, including narrow or weak AI, which is designed for a specific task, and general or strong AI, which can perform any intellectual task that a human can. AI is used in many industries to improve efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making, including healthcare, finance, and customer service.
However, it is essential to note that AI is not a replacement for human intelligence but rather an extension that can assist and enhance human capabilities. Ethical considerations around AI, such as its impact on jobs and privacy, are essential to keep in mind as it advances and becomes more integrated into our daily lives.
What Is AI Sentience in Robotics?
The notion of AI sentience refers to the ability of a robot or artificial system to have subjective experiences such as emotions, self-awareness, and consciousness. This extends beyond a robot’s capacity to complete tasks or make decisions based on algorithms and data to construct a genuinely autonomous being with its own subjective experiences and perceptions.
In robotics, AI sentience means that a robot is designed to execute particular activities and can make decisions, feel emotions, and interact with the environment in a manner comparable to that of a human being.
One example of AI sentience in robotics is the case of the AI robot named ‘Bina48’. Bina48 was created by a company called Hanson Robotics and is designed to exhibit human-like qualities such as emotions, self-awareness, and the ability to hold conversations. Bina48 was created using information and data collected from its human ‘source’, a woman named Bina Rothblatt.
The robot uses advanced AI algorithms to process information and respond to stimuli in a way that mimics human behaviour. Bina48 has been used in various experiments to test the limits of AI sentience and has been shown to exhibit a range of emotions and respond to different situations in a way that suggests a level of consciousness. This robot is a fascinating example of the potential for AI sentience in robotics and the future of AI technology.
How Does AI Sentience Work?
AI sentience in robotics would work through the implementation of advanced AI algorithms that allow robots to process and analyse information in a way that mimics human consciousness. This would involve creating a self-aware AI system that can make decisions, hold conversations, experience emotions, and perceive its surroundings in a similar manner to a human being.
The AI system would need to have a high level of cognitive processing power and be able to analyse and respond to stimuli in real-time. Additionally, the AI system would need to be able to learn from experience and adapt its behaviour accordingly, which would require the development of advanced machine learning algorithms.
To achieve sentience, the AI system would also need access to a large amount of data that it could use to understand the world and make decisions. This data could come from sensors, cameras, or other sources and would need to be processed and analysed in real-time to enable the robot to make informed decisions.
The process for creating AI sentience would be similar to the one below.
- Data Collection: The first step in creating AI sentience would be to collect vast amounts of data from various sources. This data would be used to train machine learning algorithms and help the AI system understand the world and make informed decisions.
- Pre-Processing: The collected data would then undergo pre-processing to clean, format and make it ready for use in training the AI model.
- Model Training: The processed data would then be used to train an advanced machine learning model that would enable the AI system to recognise patterns, make predictions and perform tasks.
- Model Validation: The trained model would then be tested and validated to determine its accuracy and ability to perform the intended tasks.
- Integration With Robotics: The trained and validated AI model would then be integrated into a robot or system to give it the ability to process and analyse data, make decisions and exhibit human-like qualities such as emotions and self-awareness.
- Continuous Learning: The AI sentience system would need to continuously learn and adapt as it interacts with the world, which would require the implementation of advanced reinforcement learning algorithms and the ability to access and process large amounts of real-time data.
Why AI Sentience?
AI experts are striving to achieve sentience in robotics because it would represent a significant breakthrough in the field of AI and demonstrate the ability of machines to process information and make decisions in a manner similar to human consciousness. Sentience in robots would open up new possibilities for their functionality and application, including the ability to perform complex tasks, interact with the environment in a more intuitive and human-like way, and exhibit human-like qualities such as emotions and self-awareness.
Additionally, the development of sentient robots could have important implications for fields such as healthcare, manufacturing, and entertainment by providing new and innovative solutions to existing problems. The drive to achieve AI sentience in robotics is driven by the desire to push the boundaries of what is possible with AI technology and to explore the potential of machines to change our world for the better.
One example of how AI sentience is being used in healthcare is through the development of virtual nursing assistants. These AI-powered robots are designed to assist nurses in patient care and provide patients with a more personalised and compassionate experience. The virtual nursing assistants use advanced AI algorithms to process information about a patient’s condition, symptoms, and treatment history and can provide real-time recommendations and support.
Additionally, these robots can use natural language processing and advanced conversational AI to hold conversations with patients, answer their questions, and provide emotional support. By providing patients with a more personalised and human-like experience, virtual nursing assistants can help improve patient outcomes, increase patient satisfaction, and reduce the burden on healthcare providers. This is just one example of how AI sentience is being used in healthcare to transform the delivery of care and improve patient outcomes.
There are several companies working on developing AI-powered virtual nursing assistants, but no company has yet created a fully sentient AI nurse. Some companies in this field include:
- Cogito: A company that develops AI-powered virtual assistants to improve customer engagement and support.
- Lemonaid: A company that uses AI to provide virtual consultations and prescription services.
- Woebot: A company that uses AI and machine learning to provide individuals with mental health support and counselling.
These are just a few examples of companies working on developing AI-powered virtual nursing assistants. However, it is essential to note that these systems are not fully conscious and do not possess true self-awareness or emotions. The development of AI sentience in healthcare is still in its early stages, and it may be several years before fully sentient AI systems are deployed in real-world healthcare settings.
The Risks and Challenges
The development of AI sentience in robotics is a complex and challenging field, and it comes with several risks and challenges that must be carefully considered and addressed. These risks and challenges can be broadly categorised into three areas: technical, ethical, and social.
Technical Risks and Challenges
One of the most significant technical risks and challenges of creating AI sentience in robotics is the difficulty of making a truly self-aware and conscious machine. Despite significant advances in AI technology, we are still far from fully understanding the nature of consciousness and how it arises from the interaction of neurons in the brain. To create AI sentience, we must first have a deep understanding of how consciousness works and how it can be replicated in machines.
Another technical challenge is ensuring that sentient robots are capable of making decisions that are safe and ethical. For example, if a sentient robot is programmed to prioritise its own survival over the safety of humans, it could potentially cause harm to those around it. To address this challenge, developers must carefully consider the ethical implications of their AI systems and ensure that they are programmed with the right goals and values.
Ethical Risks and Challenges
The development of AI sentience in robotics raises many important ethical questions, including guaranteeing that sentient robots treat humans with respect and dignity and safeguarding that they do not cause harm to those around them. There is also the question of ensuring that sentient robots are treated fairly and with respect and how to prevent them from being abused or exploited.
Another ethical challenge is ensuring that sentient robots have the right to privacy and freedom of thought. For example, if a sentient robot is capable of experiencing emotions and forming its own thoughts and opinions, how can we ensure that these thoughts and opinions are protected from outside interference or manipulation?
Social Risks and Challenges
Finally, the development of AI sentience in robotics raises several social risks and challenges, including ensuring that sentient robots are accepted and integrated into society and that they do not cause social or economic disruption. For example, if sentient robots become capable of performing many of the tasks that humans currently perform, it could lead to significant job loss and economic disruption.
In addition, there is the question of ensuring that sentient robots are used responsibly and ethically. For example, how can we ensure that sentient robots are not used for harmful or malicious purposes, such as in developing autonomous weapons?
Closing Thoughts
The answer to whether AI will ever become sentient is still unknown. While there have been significant advances in AI technology, experts are still divided on whether it is possible to create genuinely self-aware and conscious machines. Some believe this is a natural next step in the development of AI, while others believe that it may be technically impossible or too risky to pursue.
As for the question of whether we should let AI become sentient, opinions are also divided. Those who believe that AI should become sentient argue that it could lead to significant benefits, such as increased efficiency, improved decision-making, and the creation of new forms of intelligence. However, those who are opposed argue that the risks associated with AI sentience, such as the potential for harm to humans and the disruption of social and economic systems, are too significant to justify the development of this technology.
Ultimately, deciding whether AI should become sentient is a complex and controversial issue that requires careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks. It is crucial to have open and honest discussions about this issue and to ensure that any decisions made are based on a thorough understanding of the technology and its potential implications.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is solely the author’s opinion and not investment advice – it is provided for educational purposes only. By using this, you agree that the information does not constitute any investment or financial instructions. Do conduct your own research and reach out to financial advisors before making any investment decisions.
The author of this text, Jean Chalopin, is a global business leader with a background encompassing banking, biotech, and entertainment. Mr. Chalopin is Chairman of Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The co-author of this text, Robin Trehan, has a bachelor’s degree in economics, a master’s in international business and finance, and an MBA in electronic business. Mr. Trehan is a Senior VP at Deltec International Group, www.deltec.io.
The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in this text are solely the views of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect those of Deltec International Group, its subsidiaries, and/or its employees.